*Memory, Storage Devices and Media*
 .
.
There are three different types of storage that a computer uses:
- primary storage
- secondary storage
- off-line storage
Primary Storage
Also known as primary memory. Once the data is input into a computer, it is stored in a place that can be accessed quickly by the computer’s processor. Primary storage is a computer’s internal storage and is in storage where data is held before processing. The capacity is small and separated into RAM and ROM. Both are memory chips.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
RAM holds data to be processed and data can be written and read from. Data and programs in RAM are held temporarily and erased when they are no longer needed. Content in RAM is only removed when computer’s power is switched off so it is ‘volatile’.

The amount of RAM in a computer varies on the computer. RAM can increase
the storage capacity and it will hold the operating systems. RAM is often built into peripherals such as printers. So when the printer prints the data, the computer can move onto other tasks.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Four types of ROM
-Firmware – ROM that holds programs that run on an embedded computer. Firmware does not load if system fails.
-Bootstrap – ROM that contains startup instructions – PC/Laptop/Phone/tablet
-EPROM – Rewritable ROM – used in keyless systems and micro controllers
-Flashing – Upgrading firmware is known as flashing. ROM used on devices to recover OS/Firmware. Commonly used to erase/rewrite data to ROM
ROM is a primary storage that can be read but not written to. ROM does not lose its contents so it is ‘non-volatile’. The contents of ROM depends of the type of device. ROM tends to be smaller in capacity compared to RAM.
Certain types of ROM can be erased and re-written to. This is called the erasable programmable read only memory (EPROM). This is found when a device’s firmware needs to be upgraded.
–Embedded computers: computer that is built into a device that performs one or more specialized tasks such as a digital watch. Will have a few kilobytes of RAM, RAM will hold data for processing. It uses ROM to hold software that runs device such as amicrowave which can only complete specific functions. This is called firmware. The bios is inside the ROM which loads operating systems and tells if components are correct.
–General purpose computer: computer with many applications such as desktops PCs. Will have a few gigabytes of RAM, RAM holds operating system, running programs and data for processing.. It uses ROM to hold software known as bootstrap which contains start-up instructions for computers. Bootstrap determines the basic hardware structure of computer and instructions for loading the operating system
Secondary Storage
We need secondary storage to hold data and software on a more permanent basis. Data can be held in secondary storage until they are erased or over written. Data and operating systems must be transferred into RAM from secondary storage before processor can access them so it is not directly accessible to processor and is slower to read and write data. Secondary storage is large in capacity and can be up to a terabyte. Some devices are also removable so they can be transported between computers. There are three types of secondary storage
Magnetic storage
Device that reads write and removes data from magnetic fields which control magnetic dots of data that represents binary. They can be either tape based or disk based.


Tape based uses a cartridge of lopped magnetic tape that goes over an electromagnetic read/write head. Disk based devices is made up of several disks known as platters which are attached to a spindle which will spin at high speed. Data is read, written or erased as the dots pass under the read/write heads which are on a moving arm. The arm moves back and forth across the platter to get data from different tracks.
Many computer hard drive uses magnetic storage. Examples of magnetic storage is a hard drive, floppy disk and a tape cassette. Hard disk drives can hold up to 8 terabytes data while a magnetic tape can hold up to 185 terabytes.
Data transfer rate:
185 MB per second for hard disk drive (data can be accessed directly because read/write heads can move to the point where data is stored)
30 MB per second for magnetic tape (data stored on magnetic tape is quickly found when data required is near point at which the tape starts being read but if it is far away, it has to loop around to the correct place first)
Optical storage

Device that reads data by shining a laser beam on the surface of plastic disks. Indentations known as pits are made on the surface of the disk. Pits represent binary data. The areas in between pits are known as land. Land would be no indentation. Land is how much memory is available on a bit. The pit reflects light back from land and the optical device will tell the different between the binary 1s and 0s.
Pit Land Pit Land Pit
1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1
The process of recording data on an optical disk is called ‘burning’. Optical disks have good data transfer rate of 10-72 megabytes per second. and data stored is more portable because the disk can be carried to many locations. It has a slower data transfer rates than hard disks and lower storage capacity. Desktop PCs and laptops have a built-in optical disk drive. Different types of optical storage are compact discs (CDs), digital versatile disk (DVDs) or Blu-ray disks.
DVDs (split into single and dual layer) use a higher frequency laser than CDs so pits and lands are packed tighter onto tracks to allow more data to be stored. Blu-ray devices used a blue-violet laser. It gives more precision when writing and reading from a disk.
Optical media has different types:
- ROM, data stored is already burned onto disk. It can only be read
- R, disk is empty of data and can written to once then it can be read.
- RW, disk is empty but can be written and read from repeatedly.
-CD has a capacity of 700MB
-DVD single layer has a capacity of 4.7GB
-BLuray single layer has a capacity of 25GB
Solid-state storage
Solid-state storage: high speed flash memory is used to store data. It can be written and read to many times. This makes them useful as portable storage device. A solid state storage is non-versatile and data can be stored electronically rather than magnetically. They are small in size but data transfer rate is quicker than other types of storage of 230MB per second.
A solid state storage can be written to and from many times. They are used in many portable devices such as tablets and smartphones but it can also be found in compact media players, cameras and computers. Examples are USB, RAM sticks, SD cards or solid-state hard drives.
Off-line storage
Non-volatile storage device that is disconnected from computer (backup). This includes optical media, USB ram sticks, external hard drives and magnetic tape.
Definitions
- MIDI – (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol designed for recording and playing back music. It connects device that make and control sound so that they can communicate with each other. It also transmits information about how music is produced.
It contains files that are made up of:
- Notes that are played
- When notes need to be played, how long each note is held for or the pressure applied
- Velocity of each note
- Uses 8 bit asynchronous serial transmission with one start/stop bit
- MIDI has 16 channels to operate from
- It has pitch byte and velocity byte
When music or sound is recorded on a computer system, MIDI messages are saved in a file that can be recognised by a file extension .mid. The file can be fed back through different electronic devices but they would need to use the sequences software.
MIDI has a lower quality than mp3 (approximately 90% decrease in size of file) and it uses 8 bit serial transmission. It contains 16 channels from 0-15. The advantage of using MIDI over MP3 is the memory size is larger.
- Velocity byte – Identifies pressure or how loud a keynote should be played.
- Pitch byte – Pitch byte is used to identify which note or key has been pressed.
- Asynchronous – Not existing or happening at the same time.
- serial transmission – Process of sending data one bit at a time over a communication channel or computer bus.
- File compression – Method of reducing the file size. It is able to reduce the overall number of bits and bytes in a file so it can be transmitted faster over slow internet connections and it can take up less space on a disk.
You can compress a text file by creating a word dictionary and changing the file.
- Bit rate – the number of bits per second that can be transferred at a time.
- MPEG – (Motion Picture Experts Group) digital video compression. A compression standard used for compressing video and audio files to a smaller physical size, it also handles the transmission of these files.
- JPG – JPG is a file extension for a lossy graphics file. JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group.
Jpeg is used to reduce photographic/graphic file sizes and to reduce RAW BITMAP image factor between 5-15. Image pixels are calculated using width x height to get total file size.
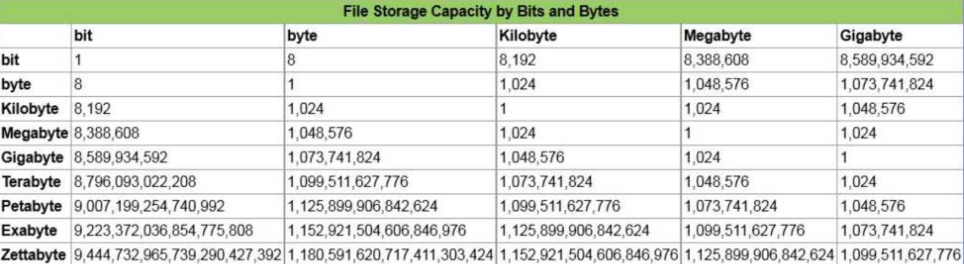
To calculate bytes to kilobytes = bytes / approximately 1000
- BMP – stands for bitmap is a graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device (such as a graphics adapter),
- PNG – (Portable Network Graphics) Portable Network Graphics is a raster graphics file format that supports lossless data compression.
- TIF – TIFF files can be saved in an uncompressed (lossless) format or may incorporate .JPEG (lossy) compression. They may also use LZW lossless compression, which reduces the TIFF file size, but does not reduce the quality of the image.
- Lossless – File is shrunk but no data is lost. Original file can be recreated when uncompressed. It breaks file into smaller pieces for storage or transmissions.
- Lossy – Unnecessary data eliminated. Commonly used with bulky files. Data that is eliminated cannot be recreated. Similar text and sound removed that humans find it hard to detect.
- Air gapped storage – Device that has never been connected to the world wide web, network security will ensure that a secure computer network is isolated from unsecured networks such as public internet.
- Cache memory – temporary memory that is high speed memory.
Choosing an appropriate secondary storage device
Factors are:
-capacity
-transfer speed
-portability
-durability
-cost
Calculating storage requirement of a file
MP3 files are reduced by 90%. You can compress an Mp3 track by removing similar sounds which changes the quality.
(1 minute is 12 MB)
(RGB makes up 3 bytes)
Images can be compressed by changing file format .bmp .jpg .png . tiff
Total bytes are converted to MB, KB and GB